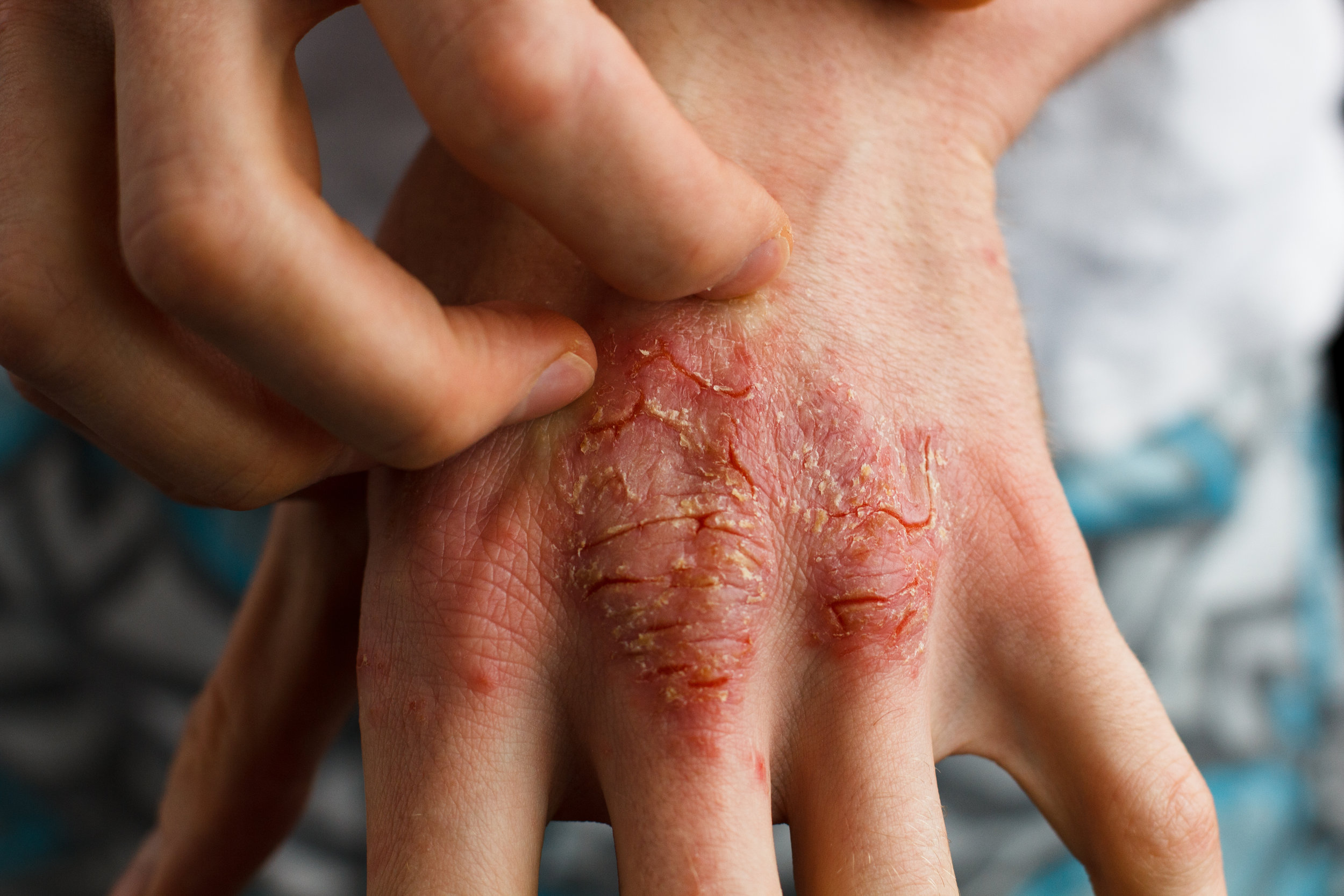
Stevens–Johnson Syndrome (SJS) is a rare but life-threatening disorder that affects the skin and mucous membranes. Often triggered by an adverse reaction to medication or an infection, this condition is both unpredictable and dangerous. Though not very common, when SJS does occur, it progresses rapidly and demands immediate medical attention. The severity of this disorder can range from painful skin lesions to full-body reactions involving internal organs. Because of its rarity, most people are unaware of the condition until it happens to them or someone they know.
In this detailed guide, we’ll explore what Stevens–Johnson Syndrome is, what causes it, how it is treated, and whether there’s any permanent cure available.
What is Stevens–Johnson Syndrome?
Stevens–Johnson Syndrome is a severe skin and mucous membrane reaction, most commonly to medications or infections. It usually starts with flu-like symptoms such as fever, sore throat, and fatigue. Soon after, the skin begins to blister and peel off, resembling a burn injury. The damage typically begins on the face, chest, or genitals and can spread rapidly.
SJS is considered a type of hypersensitivity reaction and lies on the same disease spectrum as Toxic Epidermal Necrolysis (TEN) — a more severe form where more than 30% of the body surface is affected. If 10% or less of the body is involved, it is classified as Stevens–Johnson Syndrome. When between 10–30% of the body surface is affected, it is considered an overlap between SJS and TEN.
Causes of Stevens–Johnson Syndrome
SJS can be triggered by multiple factors, but medications are the most common cause. These include:
1. Antibiotics such as sulfonamides and penicillins
2. Anticonvulsants like phenytoin, carbamazepine, and lamotrigine
3. Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) like ibuprofen and naproxen
4. Allopurinol, used to treat gout
Besides medications, some infections can also trigger SJS:
* Herpes simplex virus (HSV)
* Mycoplasma pneumonia
* Hepatitis
* HIV
In rare cases, vaccinations and certain cancers have also been linked to SJS. However, it’s important to understand that not everyone who takes these medications or contracts these infections will develop SJS — it usually depends on individual sensitivity, genetics, and immune response.
Symptoms of Stevens–Johnson Syndrome
The symptoms of SJS typically begin 1 to 3 weeks after starting a new medication or after an infection. Here’s how it usually progresses:
1. Early Symptoms (1–3 days before rash appears):
* Fever
* Sore throat
* Tiredness and body aches
* Burning eyes
* Cough and other flu-like symptoms
Later Symptoms:
* Red or purple rash that spreads
* Painful blisters on the skin and mucous membranes
* Skin that peels off, similar to a burn
* Mouth, lips, eyes, and genitals may become sore and ulcerated
* Difficulty swallowing or breathing in severe cases
* Eye redness and sensitivity to light
SJS can worsen quickly, so early recognition and hospitalization are essential.
How is Stevens–Johnson Syndrome Diagnosed?
Diagnosis of SJS is largely based on clinical appearance and patient history. Doctors may ask about:
* Recent medication use
* Signs of infections
* Family history of drug allergies
To confirm the diagnosis, doctors may perform:
1. Skin biopsy: To examine tissue under a microscope and rule out other skin conditions
2. Blood tests: To check for infections, organ function, and immune response
3. Cultures: If an infection is suspected
Because of the high risk of complications, people with suspected SJS are often referred to a burn unit or intensive care unit.
Is There Any Permanent Cure for Stevens–Johnson Syndrome?
This is a crucial and complex question. The short answer is: No, there is no permanent cure for Stevens–Johnson Syndrome in the traditional sense.
SJS is an acute condition, which means it arises suddenly and is treated as a one-time medical emergency. The goal of treatment is to stop the progression of the disease, manage symptoms, and allow the skin and body to heal. Once the acute episode is over, most people do not experience a recurrence — unless they are exposed to the same drug or trigger again.
That said, while there is no “cure,” full recovery is possible in many cases with timely and proper treatment. However, some individuals may be left with permanent complications depending on the severity of the condition.
Treatment and Recovery Process
Immediate Actions
1. Stop the suspected medication immediately
2. Hospitalization, usually in an intensive care unit or burn unit
3. Supportive care: Includes IV fluids, electrolytes, pain management, and wound care
Medications May Include
1. Corticosteroids to reduce inflammation (though this is debated)
2. IV Immunoglobulins (IVIG) to block the immune response
3. Antibiotics if secondary infections develop
4. Eye drops or ointments for eye protection
Wound Care
1. Dressings to protect open skin
2. Topical creams or antiseptics
3. Avoidance of adhesive bandages that could further damage skin
Nutritional Support
Since swallowing can become painful due to mouth ulcers, patients may need feeding tubes or specialized diets during treatment.
Long-Term Outlook and Complications
While many people recover fully from SJS, some experience long-term or even permanent complications:
1. Skin Scarring
2. Eye Damage: Dry eyes, blindness, or vision changes
3. Lung Damage: Scarring of airways leading to chronic respiratory issues
4. Organ Damage: Including kidney or liver problems in severe cases
5. Emotional Trauma: The sudden and painful experience can cause PTSD or anxiety
Therefore, even though there’s no “permanent cure” needed in the classic sense (like in chronic diseases), the possibility of lasting damage means patients must continue with long-term follow-up care, including visits to dermatologists, ophthalmologists, and mental health professionals.
Can Stevens–Johnson Syndrome Be Prevented?
Since the condition is often triggered by a medication, preventing exposure is the key to preventing a recurrence.
Precautionary Steps Include
1. Maintaining a detailed list of medications you’re allergic to
2. Wearing a medical alert bracelet
3. Informing doctors and pharmacists of your history with SJS
4. Genetic testing in certain populations (especially for those of Asian descent taking carbamazepine)
In fact, the U.S. FDA and health bodies in some countries recommend HLA-B\1502 genetic testing for Asian individuals before prescribing drugs like carbamazepine, due to a higher risk of developing SJS.
Is Stevens–Johnson Syndrome an Allergic Reaction?
Yes, in many cases, Stevens–Johnson Syndrome can be considered a severe allergic reaction, specifically a Type IV hypersensitivity reaction, also known as a delayed immune response. Unlike typical allergies that cause sneezing or itching, this reaction goes much deeper — activating T-cells that attack healthy skin cells, mistaking them for harmful invaders.
So while it’s not an “allergy” in the conventional sense (like a peanut allergy), SJS is indeed an immune system overreaction, often caused by drugs or infections. That’s why identifying and avoiding the trigger is so important to prevent another episode.
Life After Stevens–Johnson Syndrome
Surviving SJS is a major milestone, but life after the syndrome comes with challenges. Many patients need physical and psychological rehabilitation. Some tips for adjusting post-SJS include:
1. Regular checkups for vision, skin, and respiratory health
2. Sun protection for sensitive new skin
3. Counseling or therapy to manage trauma
4. Staying informed and educating family members about the condition
5. Maintaining an emergency plan and medication alert system
With the right support and medical guidance, most survivors lead full and active lives. However, they remain vulnerable to future episodes if the trigger is not avoided.
Bottom line
Stevens–Johnson Syndrome may be rare, but it is extremely serious. What starts as a simple fever or rash can quickly escalate into a life-threatening medical crisis. There’s no single permanent “cure” for SJS, but with timely treatment and preventive care, most patients can recover and avoid future episodes.
It’s vital for anyone who’s experienced this syndrome to take lifelong precautions and maintain open communication with their healthcare providers. Whether you’re a patient, caregiver, or simply someone wanting to be informed, understanding Stevens–Johnson Syndrome is a step toward better awareness and health safety.